What Is Appium?
Appium is a freely distributed opensource mobile application UI Testing framework; an ecosystem of tools and libraries. It allows native, hybrid and web application testing and supports automation tests on physical devices as well as an emulator, simulator or both. It provides cross-platform application testing, i.e., a single API works for both Android and iOS platform test scripts. Platform examples are android, iOS, desktop apps (Windows, Mac) and now on platforms like Smart TV and much more.
It supports all languages that have Selenium client libraries; examples are Java, Objective-C, JavaScript with node.js PHP, Ruby, Python, c#, etc. This means users can often use the programming language they are happier/more comfortable with when writing automated scripts/test codes. It was originally developed by Dan Cuellar in 2011, using the programming language C#, and called "iOS Auto". It is now developed and supported by Sauce Labs and can be summarised as a Cross–Platform Mobile Automation Tool.
How Does Appium Work?
It is an ‘HTTP Server’ written using a Node.js platform and uses Webdriver JSON wire protocol and creates and handles multiple WebDriver sessions for different platforms. It receives connection and command request(s) from the client; it executes that command on mobile devices. There are similarities Selenium, as the Selenium Server gets HTTP requests from the Selenium Client Libraries.
Advantages of Appium
- It can run on a variety of devices and emulators and is a very good choice for test automation
- Test codes can be written in any framework or language (these are mentioned earlier)
- The same test will work on multiple platforms
- It is open-source, freely available and easy to install
- It allows the automated testing of hybrid, native, and web applications and now supports desktop application testing
- It is a cross-platform mobile testing tool which can test on multiple platforms and use a single API for both Android and IOS platforms.
There are Disadvantages as well, for example it can run slower than other testing tools because the tests depend on the remote web driver. There is also a lack of detailed reports.
Cypress is said to be a good alternative to Appium, but it is not free opensource.
What Is Cucumber?
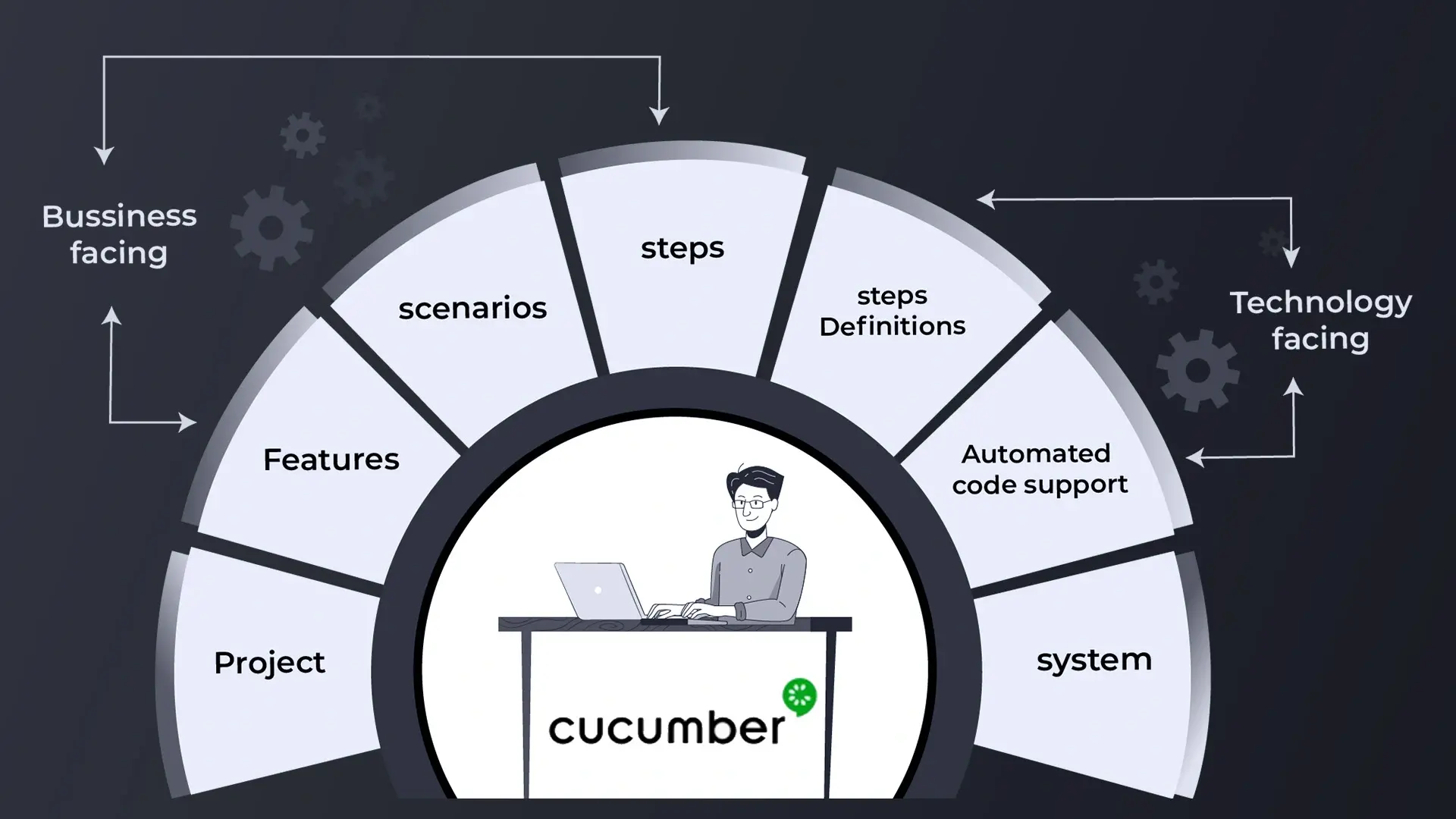
Cucumber is an open-source software testing tool written in Ruby; it supports Behaviour Driven Development (BDD). It offers a way to write tests that anybody can understand, regardless of their technical expertise. In BDD, users first write scenarios or acceptance tests that describe the behaviour of the system from the customer’s viewpoint, these are reviewed and signed off before developers write their codes. It allows automation of functional validation in easily readable and understandable format (like in simple English) which is useful for developers, testers, clients/customers etc.
What Is Jasmine?
As a behaviour-driven development framework for testing JavaScript code, Jasmine does not depend on other JavaScript frameworks. BDD (behaviour driven development) tools, are great for testing complex patterns and functions JavaScript.

What is Javascript TestRunner
How Javascript TestRunner originated; a Journey from HTML Webpages to Javascript TestRunner (which then became the Original Selenium):- In 1989 Sir Tim Berners-Lee proposed an Internet HyperText system and it was known as Hyper Text MarkUp Language (HTML) and was used for Web pages. Prior to this Text for newspapers and magazines was ‘marked up’ by editors before being sent to the typesetters, so they knew the font size, whether it would be in bold or italics and so on.
When wordprocessors appeared, they could send text straight to the printer and cut out the typesetter, the program ‘sent Text Markup Language (TML)’ to the printer; this it was similar to HTML e.g. to turn bold on and to turn it off.
Before HTML, text on computer screens looked very ordinary, however the introduction of HTML brought the text to life and could include images; the format and appearance of a webpage now looked very similar to a page in a magazine or newspaper.
In 1995 JavaScript was invented by Brendan Eich. His first version (where the languages syntax had to resemble that of Java) was completed in 10 days and called Mocha, but renamed LiveScript and then renamed JavaScript.
Scripts allowed developers to make webpages responsive and perform numerous functions/tasks etc., however, whereas before the use of scripts, webpages just needed proof-reading for ‘typos’, now they needed testing, which was done manually at first. Changes to code could cause problems - it was said to have a bug - a term used in electronics, which sometimes referred to a real bug stopping an electrical circuit from working). Testing became more intensive as webpages /web applications (WebApps) incorporated more code.
In early 1998, Brendan Eich co-founded the Mozilla project (which was free and open source), creating the mozzila.org website. The script was JavaScript, which he also created.
In 2004 a developer called Jason Huggins was working on a web application that required repetitive (manual) testing for frontend behaviour on different browsers; and he wrote a script (developed a tool) to automatically ‘Run the Test’ (amongst other things it ‘injected Javascript underneath the webpage’); he called it the JavaScript Test Runner. A Test Runner is a tool that is used to run or execute tests and export results.
To get around the requirement for JS-Injections, Jason Huggins worked with his colleague Paul Hammant to develop a server component (in Java) and TestRunner was ported to Ruby. This is how JavaScript Test Runner (open source) became the ‘Original Selenium’.


